Abstract
(1)Main Functions of Honeysuckle Polysaccharide
- Anti-inflammatory: Reduces swelling and proinflammatory cytokines, inhibits allergic contact dermatitis and rhinitis.
- Immunomodulation: Promotes lymphocyte proliferation, enhances macrophage phagocytosis, and restores normal immune function in treated mice.
- Antioxidant: Scavenges free radicals, improves neurological deficits, and protects against oxidative stress.
- Lowering Blood Lipids and Blood Sugar: Decreases blood glucose and lipid levels, improves insulin levels, and corrects lipid abnormalities.
(2)Suitable Supplement Forms
- Gummies
- Capsules
- Tablets
- Powders
- Liquid extracts
(3)Market Prospects/Advantages
- Health Benefits: Significant potential in anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, antioxidant, and metabolic health.
- Growing Demand: Increasing interest in natural and plant-based supplements.
- Versatility: Can be incorporated into various supplement forms catering to different consumer preferences.
(4)Extraction Methods
- Water Extraction and Alcohol Precipitation: Traditional method, commonly used but with low content and antioxidant activity.
- Microwave Method: Improves extraction rate but requires high-end equipment.
- Acid-Base Method: Increases extraction rate but may damage polysaccharide structure.
- Enzyme Treatment Method: Promising but needs optimization for better yield and activity.
(5)Common Specifications
- Purity levels, such as 90% or higher
- Concentration, such as specific μg/mL in formulations
- Standardized polysaccharide content for consistent efficacy

1. Health effects
A. Anti-inflammatory
Many studies have shown that honeysuckle polysaccharide has significant anti-inflammatory effects. Studies have found that honeysuckle polysaccharide has a protective effect on allergic contact dermatitis. When the dose of honeysuckle polysaccharide is 80 mg/kg, the swelling of the mouse ear decreases by 49.6%; when the dose is 20 mg/kg, the serum IgE level of the mouse decreases by 52.47%. Honeysuckle polysaccharide also reduces the level of proinflammatory cytokine TNF-α in the mouse ear tissue, indicating that honeysuckle polysaccharide has a certain inhibitory effect on allergic contact dermatitis. In addition, honeysuckle polysaccharide exerts an anti-allergic rhinitis effect by reducing the number of eosinophils, inhibiting the secretion of inflammatory factors and the expression of T cell-related cytokine mRNA in the nasal mucosa of mice.
B. Immunomodulation
Honeysuckle polysaccharide can exert immunomodulatory function. Studies have found that honeysuckle polysaccharide can promote the proliferation of mouse spleen lymphocytes. The effect is obvious at the medium concentration (100μg/mL) within the measured concentration range, and the proliferation index is 1.172, indicating that honeysuckle polysaccharide has immune activity. In addition, honeysuckle polysaccharide has a positive effect on the immune organs of mice treated with cyclophosphamide, increasing the macrophage phagocytosis rate by 30.38%, restoring NK cell activity, and restoring the levels of mouse serum cytokines IL-2, TNF-α and interferon-γ to normal, thus playing an immunomodulatory role, indicating that honeysuckle polysaccharide can be used as a potential immunomodulator.
C. Antioxidant
Honeysuckle polysaccharide has a strong antioxidant effect. Studies have found that honeysuckle polysaccharide has a strong ability to scavenge DPPH free radicals. When the concentration is 50 μg/mL, the scavenging rate is 37.3%. The cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury model confirms that polysaccharide can significantly improve neurological deficits and has a neuroprotective effect, which is related to its antioxidant capacity, mainly by inhibiting NO production, reducing malondialdehyde content, and upregulating the activity of superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase to inhibit oxidative stress-mediated.
D. Lowering blood lipids and blood sugar
Honeysuckle polysaccharide has the function of regulating blood sugar and blood lipids. A study on the hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effects of honeysuckle polysaccharide on streptozotocin-induced rats found that the fasting blood glucose level of diabetic rats taking honeysuckle polysaccharide for 6 weeks decreased by 42.71%, and the insulin level at the end of the study was 26.1 mU/L, which returned to a near normal level (24.4 mU/L), indicating that it exerts its hypoglycemic effect by improving insulin levels; total cholesterol, triglycerides and low-density lipoprotein accumulated in the plasma of diabetic rats, and high-density lipoprotein decreased. After 6 weeks of honeysuckle polysaccharide intervention, total cholesterol, triglycerides and low-density lipoprotein decreased by 46.7%, 50.0% and 70.6% respectively, and high-density lipoprotein increased by 11.26%, effectively improving lipid abnormalities.
2. Production technology
At present, the extraction methods of honeysuckle polysaccharides include water extraction and alcohol precipitation, microwave method, acid-base method, enzyme treatment method, etc. Microwave method and other extraction methods have a certain effect on improving the extraction rate of polysaccharides, but the equipment requirements are high and the implementation is difficult; although the acid or alkali extraction method can improve the extraction rate, the acid or alkali will destroy the structure of the polysaccharide. At present, the extraction of honeysuckle polysaccharides uses traditional methods, and the content of honeysuckle polysaccharides obtained by traditional methods is low, and the antioxidant activity of honeysuckle polysaccharides is poor, which needs further purification. In the future, the extraction technology with high extraction rate, mildness without destroying the polysaccharide structure and low energy consumption will be further research directions.
3. Technical content
This study takes honeysuckle as the research object, and extracts, separates and purifies honeysuckle polysaccharides. It aims to study the physicochemical properties, structural characteristics and anti-inflammatory activity of honeysuckle polysaccharides, and jointly evaluate the anti-inflammatory activity of honeysuckle polysaccharides through macrophage models and zebrafish models.
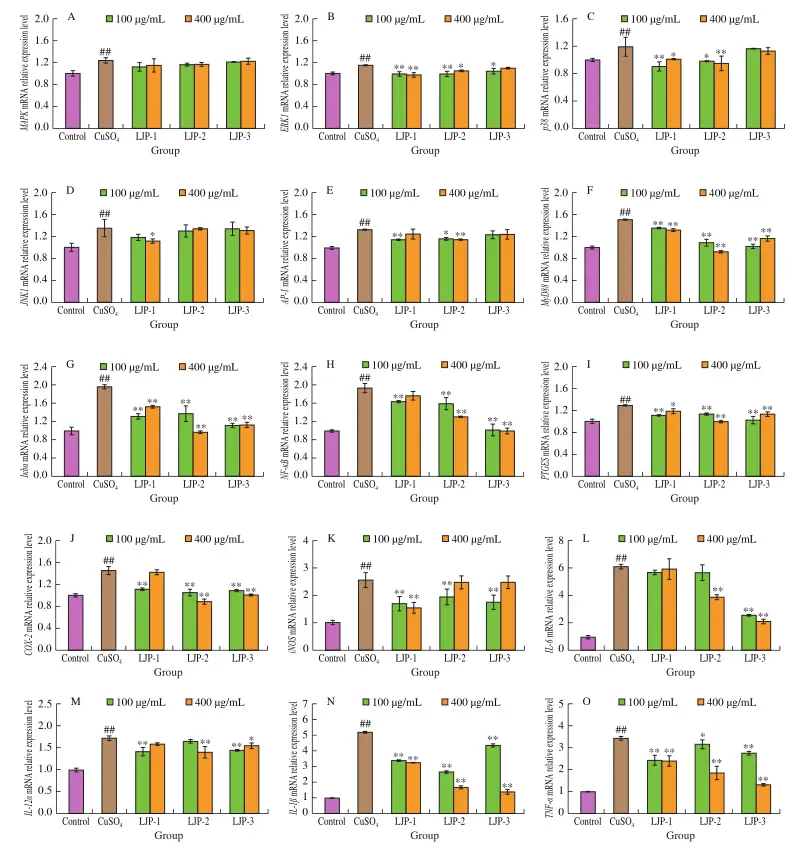
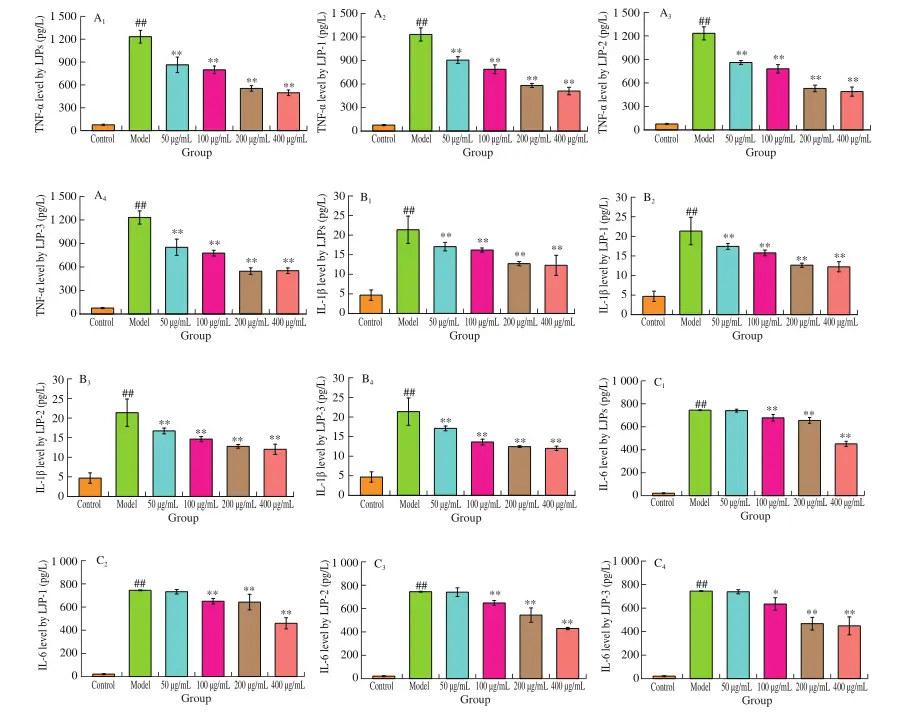
The results showed that honeysuckle polysaccharide showed significant protective effects in the lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW264.7 macrophage inflammation model and CuSO4-induced zebrafish inflammation model. Honeysuckle polysaccharide can reduce the level of inflammatory mediators, secretion of proinflammatory cytokines and expression of inflammatory proteins in the macrophage model; reduce the migration and aggregation of macrophages in the zebrafish model, and inhibit the mRNA expression levels of transcription factors, inflammatory proteins and various proinflammatory cytokines. It exerts anti-inflammatory effects through the NF-κB/MAPK signaling pathway and has good in vivo and in vitro anti-inflammatory activity. The anti-inflammatory effects of the three polysaccharide samples vary due to their different chemical compositions and molecular characteristics. Among them, LJP-2 has the most effective anti-inflammatory effect at a concentration of 400 μg/mL. The glycosidic bond of the strong anti-inflammatory LJP-2 is mainly composed of →5)-α-L-Araf (1→, →4)-α-L-GalpA (1→, →2)-α-L-Rhap (1→ residues and terminal T-β-D-Glcp. Through the above research, it is proved that honeysuckle polysaccharide is an important functional component of honeysuckle. This type of component has anti-inflammatory activity and has the potential to deliver insoluble functional components in honeysuckle.