Nutreebio has studied and analyzed the innovative raw materials used in the most popular functional food products at home and abroad, and has gained insights into the pain points of current raw material production technology. In the continuous communication with the factory, we have found corresponding technical solutions and provided them to our customers as a reference. Welcome to contact us to discuss the details of innovative technology.
1. Grape seed extract
1.1 Health effects
A. Antibacterial
GSE has strong antibacterial activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Studies have found that GSE has a strong inhibitory effect on Gram-positive bacteria such as Bacillus cereus, Bacillus coagulans, Bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus aureus, Listeria monocytogenes, and Gram-negative bacteria such as Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Salmonella typhi, and Escherichia coli. The polyphenols contained in GSE are the main substances that inhibit Escherichia coli and Salmonella. GSE with a concentration of 20% has an inhibitory effect on food spoilage and pathogenic bacteria such as Aeromonas hydrophila, Bacillus brevis, Bacillus cereus, Bacillus megaterium, Bacillus subtilis, Enterobacter aerogenes, Enterococcus, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Listeria monocytogenes, Mycobacterium, Proteus vulgaris, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus.
B. Antioxidant
GSE has a strong antioxidant function, which can remove superoxide and hydroxyl free radicals, inhibit lipid peroxidation, increase the level of antioxidants and ascorbic acid in animal blood, increase the activity of tissue catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) and superoxide dismutase (SOD), improve the ratio of reduced glutathione to oxidized glutathione and the total antioxidant status, thereby inhibiting the body's oxidative stress and reducing oxidative damage. Studies have shown that GSE can alleviate oxidative damage and reduce the damage of ethanol to the fertility, liver and brain tissue of male rats. GSE can also inhibit lipid peroxidation of unsaturated fatty acids such as α-linolenic acid, linolenic acid, eicosapentaenoic acid and arachidonic acid.
C. Anti-inflammatory
GSE inhibits proinflammatory cytokines while promoting the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines, preventing imbalance between cytokines, and showing good anti-inflammatory activity. Studies have found that GSP can inhibit the excessive production of inflammatory mediators such as nitric oxide (NO) and PGE2 by macrophages caused by endotoxin, and inhibit the expression of inducible NOS. GSP can inhibit the inflammatory response of neutrophils and prevent the adhesion and activation of neutrophils. Related studies have shown that for rats with obesity induced by a high-fat diet, GSP can reduce the levels of inflammatory markers in the liver, white adipose tissue and blood by inhibiting the production of proinflammatory factors such as C-reactive protein, IL-6 and TNF-α, promote the production of anti-inflammatory factor adiponectin, and prevent cytokine imbalance.
D. Protect cardiovascular disease
PA contained in GSE is the main active ingredient of drugs for treating various cardiovascular diseases. It has the effects of lowering blood pressure and relieving atherosclerosis, myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury, myocardial infarction, and thrombosis. Related studies have reported that GSE can increase the serum NO level of mice, inhibit the oxidation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL), reduce the levels of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and cholesterol, improve the thickness of the aortic valve, remove reactive oxygen species in the blood and arterial wall tissue, and prevent atherosclerosis. GSPE can directly quench reactive oxygen species (ROS) including free radicals and non-free radicals, reduce the sensitivity of the myocardium to ischemia-reperfusion injury, reduce the area of myocardial infarction, and improve the recovery of post-ischemic contractile function. Other researchers have found that GSP can reduce salt-sensitive hypertension in female rats by about 10 mmHg, showing a good effect in reducing arterial blood pressure.
1.2 Production technology
At present, the main methods for extracting active ingredients from grape seeds are traditional organic solvent extraction and water extraction. These two methods are simple to operate and low in cost. However, they are time-consuming, have a low yield, and have a destructive effect on the active ingredients. Solvent extraction is a traditional extraction method that uses organic solvents (such as ethanol, methanol or acetone) to dissolve the active ingredients in grape seeds. Water extraction is a method that uses water as a solvent to extract active ingredients from grape seeds. This method is simple and low-cost, but the extraction efficiency may not be as good as other technologies such as organic solvent extraction or supercritical fluid extraction. Supercritical carbon dioxide (CO2) extraction is an efficient extraction technology that can extract active ingredients without organic solvents. The extraction process is green and safe. With the advancement of science and technology, the extraction technology of grape seed extract is also constantly developing and improving to meet the market demand for high-quality and high-purity products.
1.3 Technical content
Grape seeds are rich in polyphenols and have certain antibacterial properties. They can be widely used in food, medicine, cosmetics and other fields for antibacterial properties, but their antibacterial properties need to be improved. They need to be compounded with other components to achieve the antibacterial effect. Therefore, Nutreebio and the factory have repeatedly studied and provided a method for preparing grape seed extract with high antibacterial properties. This technology uses low-temperature plasma technology to modify grape seed extract and effectively improves its antibacterial activity.
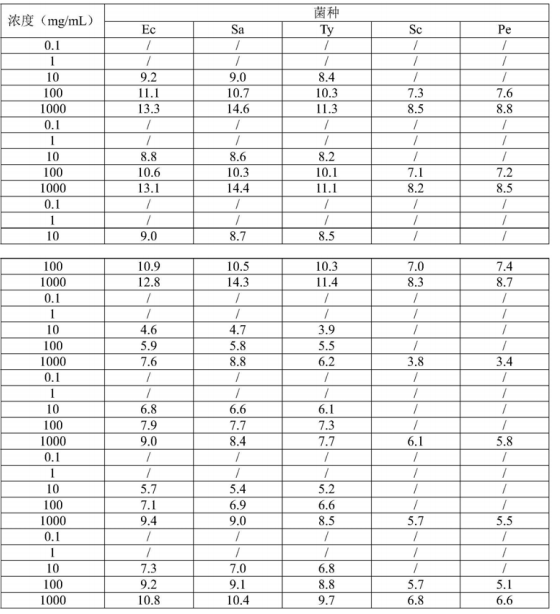
The grape seeds are crushed and sieved to obtain grape seed powder; ethanol is added to the grape seed powder, and ultrasonic extraction is performed to obtain grape seed extract; the grape seed extract is vacuum dried to obtain grape seed extract; the grape seed extract is treated with a low-temperature plasma atmosphere to obtain a highly antibacterial grape seed extract. This technology uses the high-energy particles and active components of low-temperature plasma to interact with the surface of the grape seed extract, which can modify the surface of polyphenols and other components in the grape seed extract, thereby effectively improving the antibacterial activity of the grape seed extract. The diameter of the antibacterial zone of the prepared highly antibacterial grape seed extract against five types of bacteria is nearly twice the diameter of the antibacterial zone of the grape seed extract that has not been treated with a low-temperature plasma atmosphere.
2. Cornus officinalis extract
2.1 Health effects
A. Immunomodulation
Different extracts from Cornus officinalis have different effects on the immune system. The immune excitation effect is mainly attributed to the polysaccharide components, while the immunosuppressive effect is mainly produced by the glycoside components contained. Studies have found that high and low doses of Cornus officinalis polysaccharides can significantly increase the phagocytic percentage and phagocytic index of mouse peritoneal macrophages, and can significantly promote the formation of mouse hemolysin and the transformation of mouse lymphocytes.
B. Hypoglycemic
Ursolic acid and oleanolic acid in Cornus officinalis have hypoglycemic effects on diabetic rats caused by streptozotocin. Different polar solvents were used to extract different parts of Cornus officinalis (I~V) step by step to study the hypoglycemic effects on normal mice and alloxan diabetic mice. The results showed that the extract parts III and I of Cornus officinalis can reduce the blood sugar of normal mice, and III, I, VVI can reduce the blood sugar of alloxan diabetic mice. The study also found that the total terpenes of Cornus officinalis have different effects on the blood sugar levels of normal mice, diabetic model mice and rats. The total terpenes of Cornus officinalis at doses of 100 mg·kg-1, 50 mg·kg-1, and 25 mg·kg-1 can significantly reduce the blood sugar of mice with alloxan diabetes model, increase serum insulin levels, significantly reduce the blood sugar value of rats with streptozotocin diabetes model, and increase liver glycogen content. In general, the total terpenes of Cornus officinalis have a good hypoglycemic effect on diabetic model animals.
C. Antibacterial
Studies have shown that the water extracts of Cornus officinalis pulp and core have an inhibitory effect on Staphylococcus aureus, Shigella dysenteriae, and certain skin fungi, and ursolic acid is the effective antibacterial ingredient of Cornus officinalis pulp. Cornus officinalis extract can also effectively control the growth of Candida albicans and Candida rubra. Researchers studied the stability of antibacterial activity of cornus officinalis extract and found that cornus officinalis extract had a good antibacterial effect on bacteria under the condition of pH <7, and the effect was significantly stronger than potassium sorbate; after acid and alkali treatment, the extract only had a certain antibacterial activity under acidic conditions, and alkali treatment weakened its antibacterial activity or even eliminated it; ultraviolet irradiation, temperature and common metal ions (Na +, K +, Ca2 +, Fe2 +, Fe3 +) had almost no effect on its antibacterial activity.
D. Other effects
Studies have shown that cornus officinalis extract injection has anti-shock and cardiotonic effects, total organic acids in cornus officinalis have anti-arrhythmic effects, and its cyclopentane ether terpenoids have anti-hemorrhagic shock and cardiogenic shock effects in rabbits. Vc, Ve and Se in cornus officinalis have free radical scavenging and anti-aging effects. The antioxidant effect of cornus officinalis kernel is stronger than that of pulp, and the antioxidant effects are mainly gallic acid and methyl gallate. Oleanolic acid in cornus officinalis has a liver-protecting effect. The ursolic acid in Cornus officinalis has anti-tumor effects and is clinically used for radiotherapy, post-chemotherapy leukopenia, primary liver cancer, metastatic liver cancer, cervical cancer bleeding, etc. Long-term studies by the California Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine and the Cruz Institute in the United States have shown that Cornus officinalis also has anti-AIDS effects.
2.2 Production technology
A large number of studies have confirmed that the various active ingredients in Cornus officinalis have hypoglycemic, immunosuppressive, and anti-inflammatory effects. Among them, loganin, morroniside, ursolic acid, and methyl morroniside can protect pancreatic β cells from excessive oxidative stress and apoptosis induced by high glucose, and can increase insulin release. At present, the commonly used methods for extracting the effective ingredients of Cornus officinalis are water extraction, ultrasound, alkali extraction, and microwave, but basically there are problems such as low extraction rate and incomplete extraction of effective ingredients. Enzymatic extraction is efficient and specific because it can directly act on the cell wall, degrade cellulose, pectin and other components in the cell wall, so that the cell contents are quickly dissolved and enter the extraction solvent, thereby improving the extraction efficiency and shortening the extraction time. In addition, the reaction conditions are mild, and it is not easy to destroy the active ingredients, and the cell structure is broken to the maximum extent to achieve the purpose of increasing its active ingredients. Similarly, enzymatic extraction has problems such as high cost and long extraction time. Therefore, it is necessary to develop an extraction method that can quickly and effectively extract the effective ingredients of Cornus officinalis and improve the ability to inhibit α-glucosidase.
2.3 Technical content
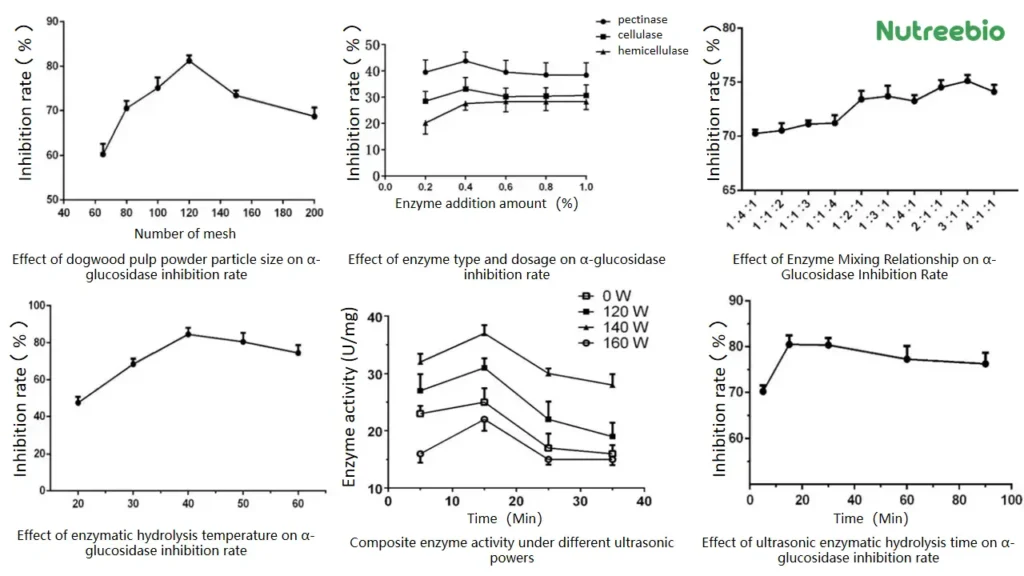
After many visits and studies, as well as experiments and research, Nutreebio finally provided a method for extracting hypoglycemic components in Cornus officinalis pulp by using ultrasonic enzymatic hydrolysis composite method. The pitted Cornus officinalis pulp is dried and crushed to obtain Cornus officinalis powder; after mixing it with enzymes and citric acid-sodium citrate buffer, ultrasonic extraction is performed at a certain power and temperature for a suitable time period; after inactivating the enzyme, centrifugation is performed, and the supernatant is the hypoglycemic component in the Cornus officinalis pulp. The method described in this technology combines ultrasonic extraction and enzymatic extraction, and performs enzymatic extraction and ultrasonic extraction at the same time, which shortens the extraction cycle and reduces the extraction cost. It is suitable for large-scale production, maximizes the utilization value and medicinal value of Cornus officinalis, and has broad market application prospects. Taking the inhibition rate of α-glucosidase as an indicator, experimental verification shows that the inhibition rate of the extracted hypoglycemic component on α-glucosidase can reach up to 83.4%.
3. Piper longum extract
3.1 Health effects
A. Anti-inflammatory
Piper longum ethanol extract can significantly reduce the total number of inflammatory cells, neutrophils, eosinophils, lymphocytes, IL-4, IL-5 and increase the expression level of IFN-γ. The chloroform extract of Piper longum can inhibit the adhesion of neutrophils to TNF-α-stimulated endothelial cells, as well as the expression of NF-κB, ICAM-1, VCAM-1 and E-selectin, and interfere with the early signals of response stimulation, further inhibiting microsomal lipid peroxidation, increasing superoxide dismutase activity and reducing malondialdehyde levels to reduce oxygen free radicals, thereby showing anti-inflammatory activity.
B. Hypolipidemia
Piper longum extract has a significant lipid-lowering effect. Hyperlipidemia is manifested by excessive blood lipid levels in the body, which leads to lipid deposition in the vascular endothelium, causing atherosclerosis, narrowing the vascular lumen, and inducing some cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases that are harmful to human health. Studies have reported that piperine can reduce serum TC and TG. Piper longum can enhance the mRNA and protein expression of HMG-CoA, CYP7A1, LCAT, and LDLR, and then regulate the liver fat metabolism process, thereby reducing serum triglycerides and increasing high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in hyperlipidemic rats, thereby achieving a lipid-lowering effect.
C. Anti-tumor
The anti-tumor effect of Piper longum involves multiple aspects such as monomer compounds, extracts and combined medication in Piper longum. Piper longum extract and its monomer components showed significant inhibitory effects on the growth of tumor cells such as liver cancer cell line HepG2, cervical cancer cell line HeLa, ovarian cancer cell line SKOV-3, prostate tumor cell line PC3, lung cancer cell line A549 and breast cancer cell line MCF7. Studies have found that piperine in Piper longum can inhibit the growth of breast cancer cells by inducing cancer cell cycle arrest and apoptosis, changing the expression of signal proteins and reducing transcription factors. Piper longum amide can inhibit STAT3 activation by upregulating cellular ROS levels, thereby regulating the Bcl-2 mitochondrial apoptosis pathway, the HIF-1α energy metabolism pathway and the CydinDl cell cycle pathway, thereby inducing breast cancer cell apoptosis.
D. Antioxidant
Studies have found that the extract of Piper longum can inhibit the oxidative stress caused by isoproterenol, and speculate that the antioxidant potential of Piper longum extract is related to its phenolic and flavonoid compounds. Some scholars have explored the antioxidant activity of Piper longum polysaccharide through ABTS and DPPH free radical scavenging experiments, and found that Piper longum polysaccharide has good antioxidant activity. In the experiment of gavage of Piper longum to rabbits with atherosclerosis, the results showed that Piper longum could increase the activity of SOD, CAT, and GSH-Px in rabbits with atherosclerosis, reduce MDA, and reduce serum TC and LDL-C levels and aortic plaque area ratio to show its antioxidant function, and the hydroxyl free radical scavenging effect showed a good dose-effect relationship with Piper longum alkaloids.
E. Protect gastric mucosa
The root extract of Piper longum can protect gastric mucosa by increasing serum GAS and mucosal PGE2 content and reducing mucosal TNF-α and TL-8 content. Studies have found that ethanol and dichloromethane extracts of Piper longum root can increase serum GAS level and P21 expression, and reduce serum TNF-α and gastric mucosal COX-2mRNA levels, thereby reducing inflammatory substances, improving gastrointestinal motility, and promoting mucosal repair. Piperine, the main component of Piper longum, can increase serum GAS content in rats with related gastritis model, protect gastric mucosa and repair damaged gastric mucosa, and can also increase P21 protein expression and reduce COX-2mRNA content to inhibit the aggravation of chronic inflammation of gastric mucosa in rats.
3.2 Production technology
The main active ingredient of Piper longum is piperine, which is generally extracted by decoction and heating reflux. The decoction method is to chop or grind Piper longum into powder, add appropriate amount of water, and stir evenly. Then heat the mixture to boiling and continue to boil for a while. Turn off the fire source to dissolve the piperine in the longan. Then filter the longan decoction to obtain an extract. However, the extraction of longan by decoction and boiling has problems such as low solubility of piperine, low extraction efficiency, and high temperature that easily leads to degradation of piperine. The heating reflux method is to grind the longan sample into powder, add it to the heating reflux device, add an appropriate amount of organic solvent, and fully soak the sample. The heating reflux device is heated to a set temperature to boil the solvent and generate steam. The steam is condensed into liquid through the condenser and then refluxed into the extraction bottle to form a cycle. After the extraction is completed, the extract is filtered to remove the solid residue, and the extract is evaporated and concentrated to evaporate the solvent, leaving the piperine solution. The heating reflux method has the defects of long extraction time, low extraction efficiency, and energy consumption. The other methods such as ultrasonic extraction or microwave-assisted extraction require relatively expensive instruments and equipment, and these instruments and equipment need to consume high electrical energy, and there are problems such as high energy consumption. During extraction, the energy of ultrasound or microwave will be converted into heat energy, causing the sample temperature to rise and piperine to degrade, affecting the extraction effect.
3.3 Technical content
Nutreebio's technology is to extract a new compound from Piper longum. Take the dried Piper longum fruit, crush it, extract and concentrate it with 95v/v% ethanol and 60v/v% ethanol by percolation method, extract it with petroleum ether and chloroform in turn, and the chloroform layer extract is separated and purified by silica gel column chromatography (petroleum ether-ethyl acetate gradient elution), silica gel column chromatography (dichloromethane-methanol gradient elution), Sephadex LH-20 and ODS-HPLC to obtain a new compound. Modern spectral techniques such as 1D-NMR, 2D-NMR, high-resolution mass spectrometry, etc. are used to identify the structure of the isolated monomer compound, and its molecular formula is inferred to be C24H33NO5, named Piper longum new alkaloid, and the molecular structure of the compound is deduced.
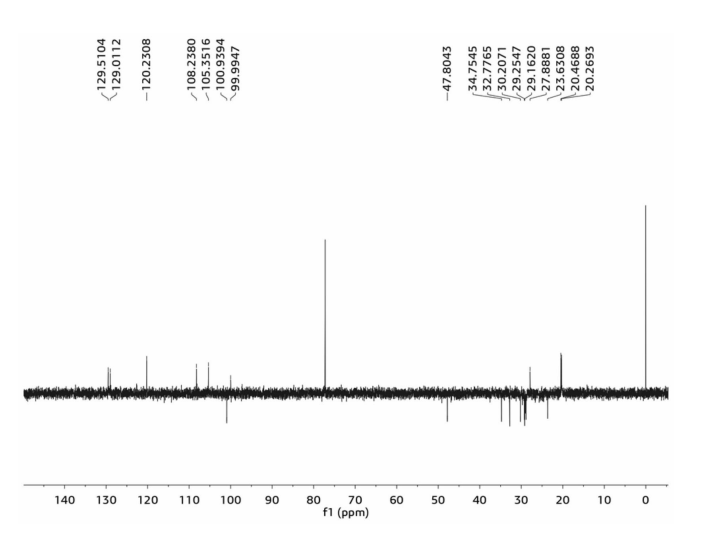
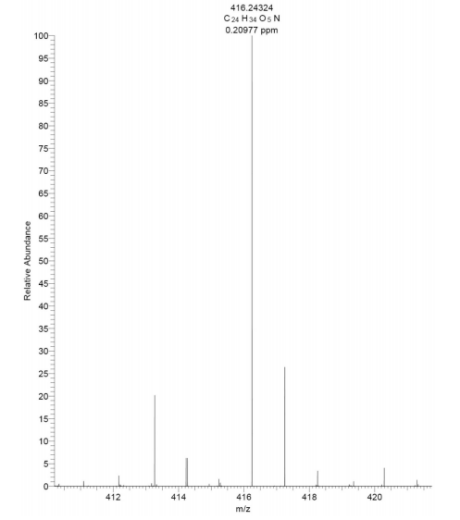
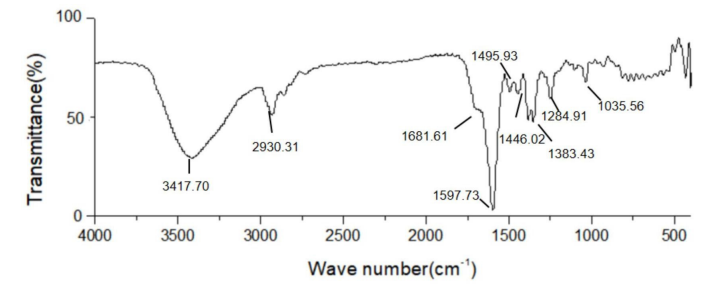
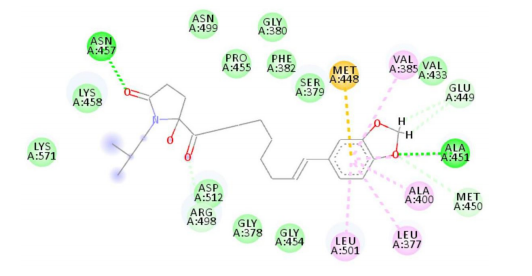
4. Apigenin A Extract
4.1 Health Benefits
A. Improve cognitive function in patients with Alzheimer's disease
This flavonoid compound from nature has attracted widespread attention in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease (AD) in recent years. AD is a chronic and gradually worsening neurodegenerative disease, whose main symptoms include memory loss, significant decline in cognitive function, and significant changes in patient behavior and personality. Although the medical community has not yet found a cure for AD, studies have shown that certain drugs and interventions can alleviate patients' symptoms to a certain extent.
Apigenin A has shown potential efficacy in improving the cognitive function of AD patients, and its mechanism of action is diverse and complex. First, it has a significant antioxidant effect, which can effectively remove free radicals in the brain and reduce the damage of oxidative stress to nerve cells. Secondly, apigenin A also has anti-inflammatory effects, which can inhibit inflammatory reactions and reduce the production of inflammatory mediators, thereby helping to slow the progression of AD. In addition, studies have also found that apigenin A can promote the expression of nerve growth factor, which helps protect nerve cells from damage and may even promote the growth and repair of nerve cells.
B. Acute ischemic stroke
The combined use of apigenin A and Danshen injection can improve the central nervous system function damage in patients with acute ischemic stroke and promote the functional recovery of patients. Studies have shown that apigenin A can block multiple pathological links of brain damage caused by ischemic stroke, has anti-cerebral ischemia effect, can reduce brain edema, improve brain energy metabolism and microcirculation and blood flow in ischemic brain areas, inhibit neuronal apoptosis, and has anti-cerebral thrombosis and anti-platelet aggregation effects.
C. Anticonvulsant
Apigenin A has a broad-spectrum anticonvulsant effect, and has an antagonistic effect on convulsions caused by electric shock, audiogenic convulsions, pentamethyl tetrazolium and corymbranaceus lactone, and can enhance the learning and memory ability of mice.
D. Protecting against retinal light damage
The mechanism of butylphthalide repairing retinal light damage mainly involves its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects. Butylphthalide can scavenge free radicals in the retina and reduce the damage of oxidative stress to retinal cells. At the same time, butylphthalide can also inhibit inflammatory reactions and reduce the damage of retinal inflammation to cells. In addition, butylphthalide also has a neuroprotective effect, which can promote the survival and regeneration of retinal nerve cells and accelerate the repair process of retinal light damage.
4.2 Production technology
In terms of production, the production technology of apigenin (butylphthalide) is relatively mature, and many chemical companies are able to produce it on a large scale. Production companies continuously optimize the production process to improve the production efficiency and product quality of apigenin to meet market demand. According to patent search, butylphthalide does not have a compound patent, and its indication patent for acute ischemic stroke has expired in 2019.
4.3 Technical content
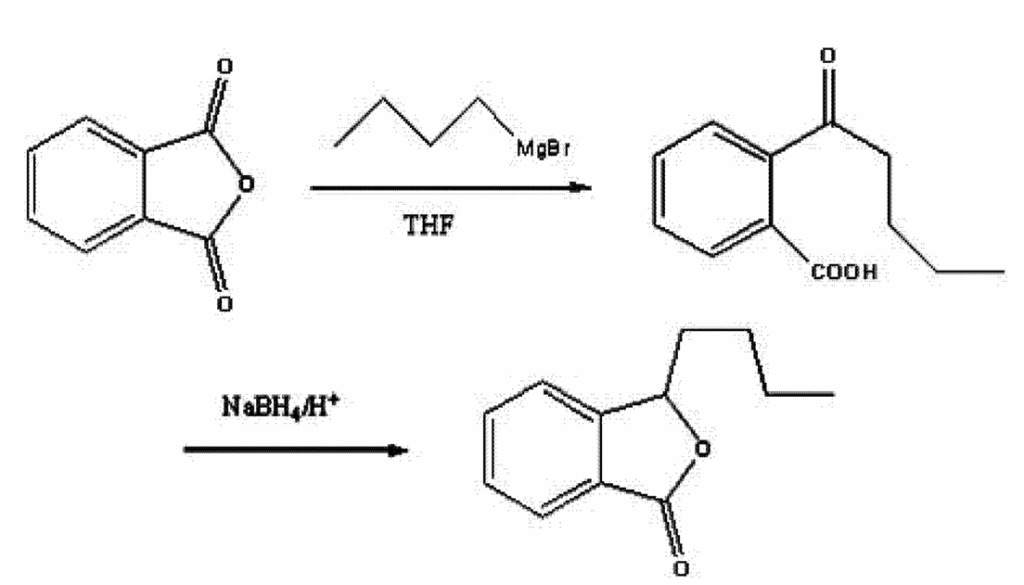
The preparation method discussed by Nutreebio with domestic and foreign authorities is to use phthalic anhydride as a raw material, and obtain the intermediate of o-valerylbenzoic acid by adding a Grignard reagent with a halogenated butane, and then obtain apigenin by sodium borohydride reduction and acid cyclization. Nutrebbio's preparation method of apigenin uses raw materials phthalic anhydride and halogenated butane, which are both commercial products, and the reaction raw materials are easy to obtain.
The preparation steps of apigenin A are as follows:
(1) Preparation of halogenated butane Grignard reagent
Under nitrogen protection, add 200ml of tetrahydrofuran, 6g (0.25mol) of magnesium flakes and 0.1g of iodine to a 500ml four-necked flask equipped with an electromagnetic stirrer, a thermometer and a reflux condenser with a drying tube, heat to 50°C, dropwise add halogenated butane (0.23mol) dissolved in 40ml of tetrahydrofuran, control the temperature at 50~70°C, continue stirring for 1h after the addition is complete, and obtain the halogenated butane Grignard reagent;
(2) Preparation of o-valerylbenzoic acid
Under nitrogen protection, add 300ml of tetrahydrofuran, 30g of phthalic anhydride and 2.5g of copper salt to a 1L four-necked flask, cool to -20~-5°C, dropwise add step (1) The obtained halogenated butane Grignard reagent was added dropwise over a period of about 1 hour. After the addition was completed, stirring was continued for 2 hours. 1 mol/L hydrochloric acid solution was added to hydrolyze to a pH of 2. The water layer was separated and the water layer was extracted twice with methyl tert-butyl ether. The organic phases were combined and washed with saturated sodium chloride solution until neutral. The phases were dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure to obtain crude o-valerylbenzoic acid.
(3) Preparation of apigenin A
160 g of 5% sodium hydroxide solution and the crude o-valerylbenzoic acid obtained in the above step (2), stirred at room temperature for 1 hour, cooled to 0°C, slowly added 6g sodium borohydride, controlled the temperature to 0°C~10°C, continued stirring at room temperature for 1 hour after the addition was completed, then added 6mol/L HCl to acidify to pH 4, extracted the water layer with methyl tert-butyl ether three times, combined the organic phases, washed with 5% sodium bicarbonate and saturated sodium chloride solution to neutrality, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and distilled under reduced pressure to obtain apigenin A.
Since the Grignard reaction, sodium borohydride reduction and acid cyclization are all classic reactions, the operation is simple and easy to industrialize, and the yield of apigenin A is 50~60%, and the purity is 97~98%.
5. Corosolic acid extract of Lagerstroemia indica and its derivatives
5.1 Health effects
A. Hypoglycemic
The active ingredients with hypoglycemic effect in the effective ingredients of Lagerstroemia indica are corosolic acid, total triterpenes and ursolic acid. The anti-diabetic effect of Lagerstroemia indica is mainly through the mechanism of inhibiting α-glucosidase and protecting pancreatic β cells, which can reduce blood sugar. The pentacyclic triterpene acid active components of Lagerstroemia indica ethyl acetate extract, including oleanolic acid, arjunolic acid, linalic acid, hawthorn acid, corosolic acid, and 23-hydroxyursolic acid, have inhibitory effects on α-amylase and α-glucosidase. Among these six compounds, corosolic acid has the strongest inhibitory effect on α-glucosidase, with an IC50 value of 3.53 μg/ml. The hot water extract of Lagerstroemia indica leaves has a protective effect on 3-morpholinoketimine-induced oxidative damage of HIT-T15 Syrian hamster pancreatic β cells. LWE protects HIT-T15 cells from oxidative damage induced by SIN-1 by promoting insulin secretion in normal HIT-T15 cells, improving the insulin secretion capacity of HIT-T15 cells caused by oxidative stress, and inhibiting lipid peroxidation and reactive oxygen species levels. Giving capsules containing Lagerstroemia extract to diabetic patients found that Lagerstroemia extract has a blood sugar lowering effect, and the blood sugar lowering effect of soft capsules is better than that of hard capsules.
B. Lipid reduction
When studying the effect of Lagerstroemia in treating type II diabetes, it was found that female mice taking feed containing Lagerstroemia extract had an anti-obesity effect. After feeding 5-week-old female KK-AY mice with a feed containing 5% Lagerstroemia extract for 12 weeks, it was found that compared with the control group fed with cellulose, the mice's food intake did not change during the feeding period, but their body weight and adipose tissue were significantly lower than those of the control group. Although they did not observe that Lagerstroemia extract had a significant effect on lowering blood sugar, the mice fed with Lagerstroemia extract had a significant decrease in blood cell ALC; although the blood lipid content did not decrease significantly, the liver fat content decreased by 65% compared with the control group. They believed that this was caused by the reduction in triglyceride accumulation, indicating that Lagerstroemia extract has a fat-reducing effect.
C. Antioxidant
The water extract of Lagerstroemia indica has a strong antioxidant effect in the linoleic acid system, and its antioxidant effect is stronger than that of α-tocopherol at the same concentration; its ability to quench DPPH and O 2-free radicals is also stronger than that of α-tocopherol at the same concentration; its ability to inhibit lipid peroxidation is basically equivalent to that of L-ascorbic acid. They also conducted antioxidant tests on the ethanol extract of Lagerstroemia indica leaves and found that it has the activity of inhibiting XOD. When the ethanol extract was purified by macroporous resin HP-20, it was found that its antioxidant function was enhanced. When analyzing the antioxidant activity of 15 Japanese health teas, it was found that Lagerstroemia indica tea has a strong effect of quenching DPPH free radicals. All components of Lagerstroemia indica can effectively eliminate superoxide anion free radicals, inhibit the recruitment of neutrophils and thus reduce inflammatory reactions, and the extracts of ethyl acetate and ethanol have stronger antioxidant activity than the extracts of methanol and water.
5.2 Production technology
The extract of Lagerstroemia indica has the functions of lowering blood sugar, lowering blood lipids, and anti-tumor. Its main functional component for lowering blood sugar is corosolic acid. Corosolic acid belongs to the pentacyclic triterpenoid compounds and is a derivative of ursolic acid. Corosolic acid is odorless and tasteless and soluble in polar organic solvents such as hot ethanol. Corosolic acid has a complex structure and is difficult to synthesize artificially. It is extracted from plants both at home and abroad. However, the existing technologies for extracting corosolic acid all have problems such as heavy pollution in the preparation method, low purity of the finished product, and low purity of the obtained product.
5.3 Technical content
In view of the shortcomings of the original technology, Nutreebio currently provides a method for extracting corosolic acid from Lagerstroemia indica. This method not only has a simple preparation process, high separation and purification efficiency, and is easy to industrialize, but also has high purity and low production cost of the prepared corosolic acid, which is suitable for large-scale industrial production. Using plants containing corosolic acid as raw materials, 10 times the dry weight of the plant is used to boil for 2 hours, the extracts are combined, filtered, and the filtrate is vacuum concentrated into an extract. Add 50% ethanol solution to the residue, adjust the pH value of the solution with sodium hydroxide, extract at 30°C, adjust the pH value of the filtrate to 4.5, let it stand for aging, separate the solid and liquid, and the precipitate is the crude total triterpene acid. Then use macroporous adsorption resin for purification, slowly cool until corosolic acid crystals begin to precipitate, refrigerate, let it stand for crystal growth, and the solid-liquid separation precipitate is corosolic acid. And the above extract can be used to further prepare oral medicines with expectorant, antitussive, antiasthmatic, Xiaoyan or hypoglycemic effects.
Precautions: Nutreebio's technology in this article was jointly studied by many well-known people at home and abroad. The content of the article is for reference only. If there is anything wrong, please leave a message to correct and communicate. And readers should not take action based on the content of the article without specific professional advice. The operator is not responsible for the losses caused by this.


