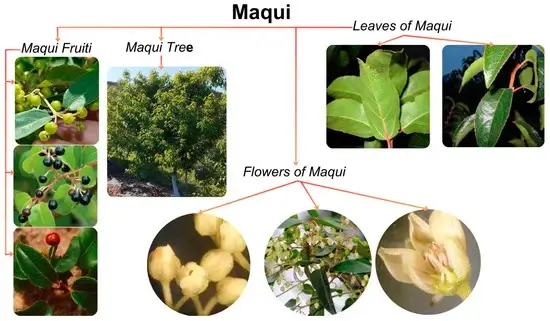
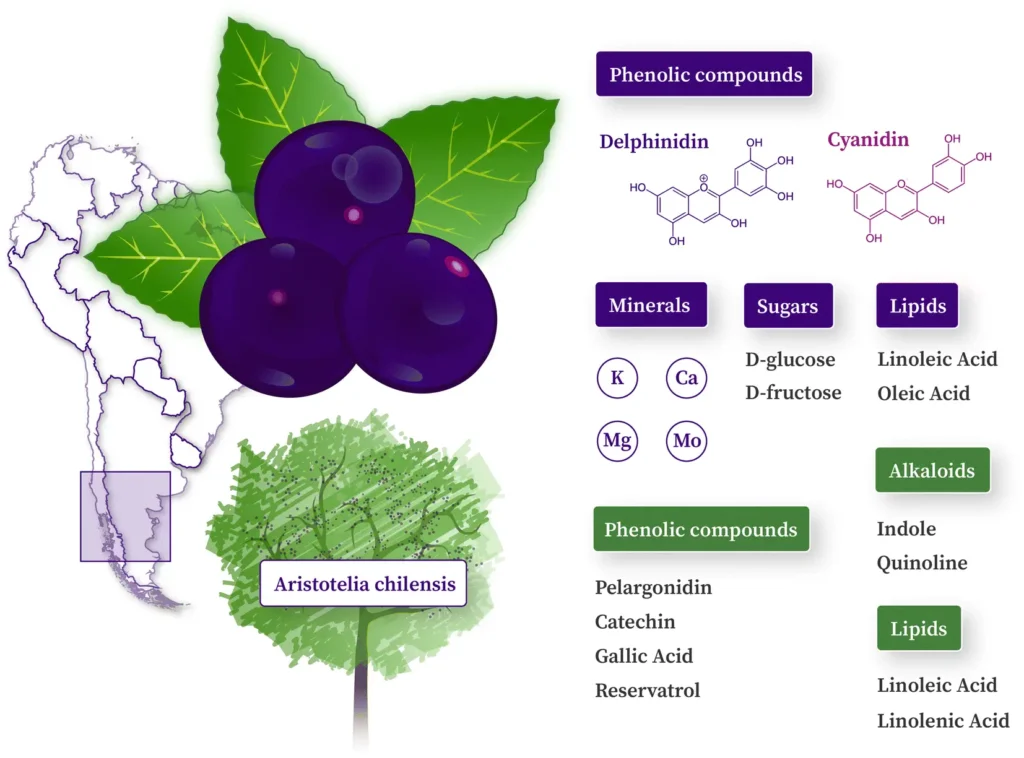
Maquiberry, also known as maqui fruit, is the purple-black fruit of the maqui tree (Aristotelia chilensis) of the Elaeocarpaceae family. It is native to the temperate rainforests of Chile and southern Argentina and is distributed in tropical and temperate Asia, Australia, the Pacific region and South America.
1. Maqui berry: the king of antioxidants among fruits
For centuries, the indigenous Mapuche Indians in the Patagonia region of South America have used the medicinal and health benefits of maqui berry to enhance physical strength, endurance and promote healthy aging. Maqui berry is revered as the "Patagonia super fruit" for its significant antioxidant properties.
According to the Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity (ORAC) Database of Specific Foods published by the U.S. Department of Agriculture, the antioxidant capacity of maqui berry is 7 times that of acai berry and 9 times that of wolfberry [1]. In addition, the database results of Brunswick Laboratories in Boston, the world's leading antioxidant capacity analysis agency for food and medicine, also show that maqui berry has the highest ORAC 5.0 value (referring to the comprehensive value of five anthocyanins) among all fruits and vegetables, making it the well-deserved "king of antioxidants".
Abroad, Italy has approved the use of maqui berry fruit as a food ingredient, and in the European Union, its fruit is also used in food supplements. Maqui berry anthocyanins are made from maqui berry fruit through water extraction, filtration, purification, concentration, drying and other processes (total anthocyanins ≥ 35%), and can be used in dairy products, beverages, jellies, chocolate products, candies and other foods. The recommended consumption is ≤ 900 mg/day (based on a total anthocyanin content of 35g/100g, and the amount exceeding this content is converted according to the actual content).

2. Composition and function of maqui berry anthocyanins
Maqui berry anthocyanins are the main components of polyphenol compounds isolated from its fruit, accounting for more than 80% of the total polyphenols [2]. There are 9 types of anthocyanins that have been isolated and identified so far, among which delphinidin-type anthocyanins are the most prominent, accounting for more than 75%[3]. Anthocyanins are controversial due to their absorption efficiency in the body, and it is generally believed that their bioavailability is relatively low, about 1%[4]. This limitation may be due to insufficient uptake by intestinal cells, low absorption efficiency, and instability in the intestinal environment. However, a study conducted on 12 subjects observed that after taking maqui berry extract, the level of anthocyanins in the participants' plasma increased significantly[5], indicating that maqui berry anthocyanins have high bioavailability in the body and can be quickly absorbed and participate in metabolic processes. This not only reveals the health benefits of maqui berry, but also provides a new direction for the research of anthocyanins. In terms of biological activity, anthocyanins have a variety of pharmacological effects, including inhibiting low-density lipoprotein oxidation, anti-skin photoaging, anti-platelet aggregation, prevention of atherosclerosis, cardioprotection, obesity control, and hypoglycemic functions.
A. Blood sugar reduction
In studies on type 2 diabetes and obesity, maqui berry dietary supplementation has been shown to significantly regulate blood sugar metabolism in experimental animals and human subjects. Studies have shown that oral administration of maqui berry anthocyanins (delphinidin-3-O-saburobiol-5-O-glucoside) can improve fasting blood sugar levels and glucose tolerance in hyperglycemic obese C57BL/6J mice. In addition, maqui berry anthocyanins have a regulatory effect on the insulin signaling pathway, especially in the negative regulation of glucose-6-phosphatase (G6Pase), thereby reducing hepatic glycogen production and glucose production [6].
In clinical studies, diabetic patients took 180 mg of maqui berry extract Delphinol® daily for three consecutive months, and their average blood sugar levels decreased by 5% [7]. This effect may be related to Delphinol®'s inhibitory effect on intestinal glucose absorption, enhanced incretin effect, and increased sensitivity to insulin [8].
B. Protect the skin
Excessive exposure to ultraviolet rays (UVB) from the sun can cause premature aging of the skin. Studies have found that delphinidin can block the phosphorylation pathways of MKK4-JNK1/2, MKK3/6-p38, and MEK-ERK1/2 induced by UVB, thereby inhibiting the activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPKs) signaling pathway and reducing the expression of MMP-1, which helps slow down the skin aging process. In addition, delphinidin glycosides can also reduce the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) by inhibiting the activity of NADPH oxidase (NOX), helping to protect skin cells from oxidative damage [9].
C. Cardiovascular health
Platelets are anucleated blood cells whose key functions are hemostasis and anti-inflammation, but excessive aggregation may lead to cardiovascular disease. The study by Yang et al. revealed for the first time that delphinidin anthocyanins in maqui berry can significantly inhibit the aggregation of human and mouse platelets and weaken thrombosis under arterial and venous shear stress, thereby helping to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease [10]. In addition, studies have found that maqui berry anthocyanins prevent heart damage caused by reperfusion arrhythmia and failure to restore sinus rhythm by reducing lipid oxidation and lowering the levels of substances that react with thiobarbituric acid and the lipid peroxidation index [11].
D. Protecting the eyes
Studies have shown that the anthocyanin components in maqui berry (delphinidin-3-O-sambubioside-5-O-glucoside and delphinidin-3,5-O-diglucoside) can effectively reduce retinal cell death caused by blue light irradiation, prevent mitochondrial fragmentation, and restore impaired oxygen consumption rate. In addition, these anthocyanins can inhibit the increase in ATF4 protein expression induced by blue light, reduce the permeability of lysosomal membranes, and thus protect the integrity of lysosomes, showing the potential of being a natural protector for preventing retinal diseases and maintaining visual health [12].
In addition to protecting retinal cells, maqui berry anthocyanins can also improve dry eye symptoms caused by insufficient tear secretion. A four-week study showed that taking 60 mg of MaquiBright® maqui berry extract (containing 25% delphinidin) daily can increase tear secretion, reduce eye fatigue, and relieve dry eye discomfort [13].

3. Multi-field application of maqui berry anthocyanins
Maqui berry is marketed as a super fruit due to its high antioxidant content and health benefits. It is used in many industries such as food, beverages, nutritional supplements and skin care products to meet the diverse needs of consumers. HP Ingredients, as the first company to introduce maqui berry to the United States, has launched a series of maqui berry products, including concentrated juice, whole fruit powder, liquid concentrate powder and standardized extract MaquiCare® (8% delphinidin, 10% anthocyanins).
A. Ordinary food
Rishi Herb Lab has launched a maqui berry sparkling tea, in which the maqui berry provides unique wine-like properties, which is a perfect alternative to a glass of wine, which can enhance vitality, detoxify and cleanse.
Andes Mountain Water has launched a 500 ml bottle of maqui berry flavored water with the benefits of maqui berry.
Navitas Organics' maqui berry powder can be used in drinks and smoothies. Sprinkle it on ice cream or infuse it into baking and frosting for a naturally vibrant purple color.
B. Dietary supplements
In 2015, Japanese scientists discovered that oral supplements made from maqui berry extract support healthy tear production and are a safer alternative to artificial tears. Life Extension's maqui berry oral nutritional supplements are added with MaquiBright® (active ingredient: maqui berry anthocyanins), which helps support healthy vision, naturally moisturize the eyeball, and keep the eyes comfortable all day.
Fitness Health Concentrated Maqui Berry Tablets contain the important ingredient 80 mg of maqui berry extract (containing 25% anthocyanins), which can help support overall health.
4. Market prospects of maqui berry anthocyanins
According to Market Data Forecast, the global maqui berry market size will reach US$1.12 billion in 2024 and will grow to US$1.76 billion by 2029, with a compound annual growth rate of 9.5% during the forecast period. Growing health awareness and rising demand for superfoods around the world have driven the consumption of maqui berry. The challenges facing the maqui berry market are mainly reflected in two aspects: price fluctuations and lack of consumer awareness. Since maqui berry is native to specific regions in South America, limited growing areas lead to limited supply, while changes in import and export regulations may affect prices, thereby limiting market expansion. In addition, the maqui berry market is relatively niche, consumers have limited awareness of it, and the high cost limits its popularity among price-sensitive consumer groups. It is worth noting that regulatory barriers related to the approval of maqui berry as a new food ingredient in different countries also pose a challenge.


