Abstract
(1)Main Functions of Purslane Polysaccharide
A. Improving Immunity
- Enhances the phagocytic ability of macrophages and releases immune factors.
- Improves humoral and cellular immunity levels, and has potential as an immune adjuvant for vaccines.
- Promotes intestinal immune regulation by increasing IL-6 release and bone marrow cell proliferation.
B. Anti-tumor
- Inhibits the growth of cervical cancer cells and induces apoptosis.
- Activates the TLR4-PI3K/AKT-NF-κB signaling pathway to protect against tumor-induced apoptosis.
- Selenized purslane polysaccharide enhances colon nutrition and anti-cancer effects.
C. Hypoglycemic
- Lowers blood glucose levels and increases insulin sensitivity.
- Stimulates insulin secretion from β-cells and reduces levels of inflammatory markers like TNF-α and IL-6.
- Acts as a potential treatment for diabetes with significant pharmacological effects.
D. Anti-inflammatory
- Reduces inflammation by inhibiting COX-2 protein and STAT3 phosphorylation.
- Balances T lymphocyte subsets and regulates inflammatory factors to alleviate intestinal inflammation.
- Improves intestinal flora balance and reduces colitis symptoms.
(2)Suitable Supplement Forms
- Capsules: For easy consumption and precise dosing.
- Tablets: Convenient form for daily intake.
- Powders: Can be mixed with food or drinks for versatility.
- Liquid Extracts: Quick absorption and easy to consume.
- Gummies: Popular and enjoyable form, especially for those who prefer a chewable option.
(3)Market Prospects/Advantages
- Health Benefits: Significant potential in immunity enhancement, anti-tumor activity, blood glucose regulation, and anti-inflammatory effects.
- Growing Demand: Increasing interest in natural, plant-based supplements with multiple health benefits.
- Versatility: Can be formulated into various supplement forms to cater to different consumer preferences.
- Safety and Efficacy: Proven benefits with minimal side effects, making it an attractive option for health supplement markets.
(4)Extraction Methods
- Cellulose Anion Exchange Column Chromatography: For purifying polysaccharides while removing impurities.
- Gel Column Chromatography: Separates polysaccharides of different shapes and sizes.
- Ultrafiltration: Uses membrane separation technology to separate molecules by molecular weight without affecting the polysaccharide structure.
- Dialysis: Removes small molecules while retaining polysaccharides through a semipermeable membrane.
- Alcohol Precipitation: Fractionates polysaccharides for further purification.
(5)Common Specifications
- Purity Levels: Typically standardized to ensure high concentrations of active ingredients.
- Molecular Weights: Examples include 64100 Da and 21000 Da for different polysaccharide fractions.
- Formulations: Available in various forms like powders, extracts, and hydrolysates for different applications.

1. Health effects
A.Improving immunity
Portulaca polysaccharide has an immune-enhancing effect. Studies have found that Portulaca polysaccharide can improve the phagocytic ability of macrophages, while releasing related immune factors to enhance the immune activity of macrophages. Portulaca polysaccharide effectively improves the humoral immunity and cellular immunity levels of tumor-bearing mice, as well as the possible molecular mechanism of immune enhancement, and is an effective adjuvant nutritional supplement for DC vaccines. Antigens treated with Portulaca polysaccharide have a certain promoting effect on the immune function of mice, and as a new immune adjuvant, it can be used in combination with DC vaccines for breast cancer treatment. Pectin polysaccharides are extracted from herbal plants such as Portulaca oleracea. Studies have shown that this polysaccharide can increase the release of IL-6 through PP-mediated bone marrow cell proliferation, thereby playing an intestinal immune regulation activity. It is worth noting that Portulaca polysaccharide can effectively activate normal immune cells.
B.Anti-tumor
The good anti-cancer activity of Portulaca polysaccharide has attracted more and more attention from scholars. The study found that purslane polysaccharide has good anti-tumor activity, can inhibit the growth of cervical cancer cells in vitro and in vivo, and is concentration- and time-dependent. It also has a protective effect on tumor-induced intestinal DC apoptosis by activating the TLR4-PI3K/AKT-NF-κB signaling pathway. The selenization of covalently selenized purslane polysaccharide PPS can incorporate inorganic selenium into the final PPS product, change its monosaccharide composition, and give it enhanced colon nutrition and anti-cancer effects. The study found that purslane polysaccharide can effectively inhibit the malignant proliferation of cells, causing obvious apoptosis of cells, and showing a dose-dependent manner; and found that purslane polysaccharide mainly induces G1 phase cycle arrest, thereby inducing cell apoptosis; in addition, the study measured the changes in tumor size and body weight in U14 mice, and the results showed that purslane polysaccharide can effectively inhibit the growth of tumors in vivo, and some purslane polysaccharide components significantly increased the weight of mice.
C.Hypoglycemic
Purslane polysaccharide has a hypoglycemic effect and is the best food for diabetic patients. The role of voltage-gated sodium channels in purslane polysaccharides and their mechanism related to insulin secretion. Purslane polysaccharides can induce insulin secretion from insulin-secreting β cell line cells (INS-1). It proves the potential of purslane polysaccharides as a diabetes treatment drug and the potential of VGSC as a diabetes treatment target. Studies have shown that purslane polysaccharides have significant pharmacological effects on diabetic rats. It can reduce the fasting blood glucose level of rats and increase their fasting serum insulin level and insulin sensitivity index value. In addition, the polysaccharide can also effectively reduce the levels of TNF-α and IL-6 and the activity of MDA and SOD in rats, suggesting that the anti-diabetic effect of CPOP may be related to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
D.Anti-inflammatory
The occurrence of diseases is often accompanied by the occurrence of inflammation. A large number of studies have shown that purslane polysaccharides have good anti-inflammatory activity. COX-2 protein and STAT 3 phosphorylation levels are both increased in colitis and decreased after purslane treatment, indicating that these two proteins are closely related to the protective effect of purslane polysaccharides, and purslane has a certain anti-inflammatory effect. Purslane polysaccharides can alleviate DSS-induced intestinal inflammation by inhibiting the expression of TLR4 and its downstream key proteins MyD88 and NF-κB in the intestinal mucosa of UC mice, inhibiting the maturation of intestinal DCs, balancing T lymphocyte subsets, and regulating the level of inflammatory factors. In addition, it can also improve DSS-induced intestinal flora imbalance.
2. Production technology
The polysaccharide components in plants contain inorganic salts, small molecules insoluble in alcohol, pigments, oligosaccharides and polymers. These substances have a certain effect on the biological activity of polysaccharides. These impurities are removed without destroying the structure of polysaccharides and affecting the biological activity, and the biological activity of polysaccharides is maintained. Common methods for purifying polysaccharides include cellulose anion exchange column chromatography, gel column chromatography, quaternary ammonium salt precipitation, precipitation, ultrafiltration and dialysis. Dialysis is a common method for removing small molecules. It is separated by concentration difference rather than pressure difference through a semipermeable membrane with a certain pore size. Small molecules are transmitted and large molecules of polysaccharides are retained. The working principle of the ultrafiltration method is based on membrane separation technology, which can separate molecules with different molecular weights. Ultrafiltration has little effect on the structure of polysaccharides, and the equipment and operation are simple and pollution-free. Gel column chromatography can separate polysaccharide molecules of different shapes and sizes. During the separation process, large molecular polysaccharides have a short path and small molecular materials have a long path, so large molecules flow out first and small molecules flow out of the gel column later.
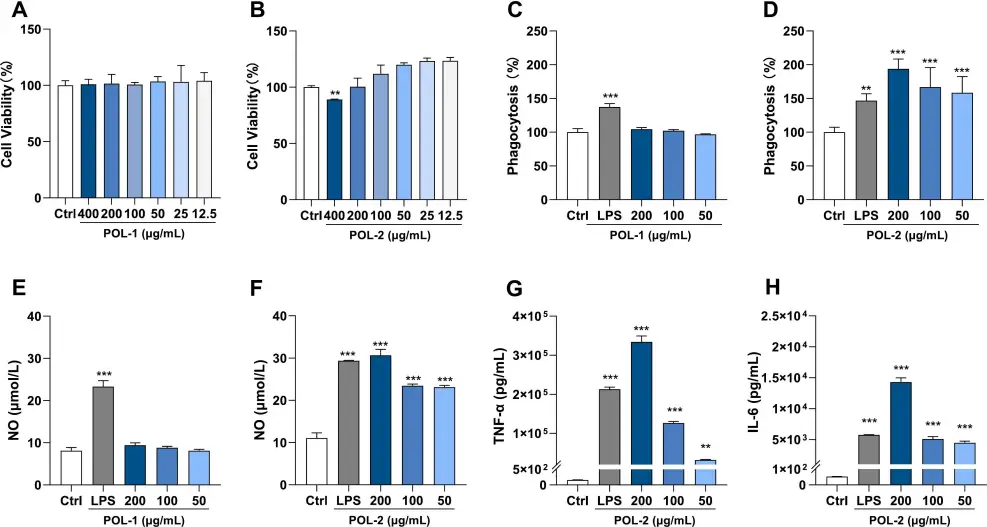
3. Technical content
Our study took Purslane as the research object, purified two water-soluble polysaccharides in Purslane, studied their structural characteristics, and evaluated their immunomodulatory activity using the RAW264.7 macrophage model. The weight-average molecular weights of POL-1 and POL-2 are 64,100 Da and 21,000 Da, respectively. Transmission electron microscopy results show that POL-1 is a non-branched single chain, while POL-2 is a microstructure entangled with side chains. Two water-soluble polysaccharides POL-1 and POL-2 were separated and purified by alcohol precipitation fractionation and DEAE anion exchange chromatography. RAW 264.7 macrophages were used to evaluate the immunomodulatory activity of purified purslane polysaccharides. Compared with the control group, POL-1 had no inhibitory effect on cell viability in the concentration range of 12.5–400 μg/mL, while POL-2 significantly inhibited cell proliferation in the concentration range of 400 μg/mL. After POL-2 stimulation, more neutrophils entered the cells, and POL-2 enhanced the phagocytosis of RAW264.7 cells. The polysaccharide POL-2 can activate the NF-κB signaling pathway by promoting the phosphorylation of P65 and IκB-α, resulting in a significant increase in the secretion of NO, TNF-α, and IL-6 in RAW264.7 cells, thus showing potential immunomodulatory activity.