1. Key Ingredients in Gummies
1.1 Gelatin, Plant-Based Gels, and Pectin in Gummies
The texture of gummies is significantly influenced by the ratio of gelatin, plant-based gels, or pectin used. Generally, there is a direct relationship between the concentration of these gelling agents and the firmness of the gummy:
Gelatin, derived from animal collagen, is a staple in gummy production for its ability to create the classic chewy texture. Increasing the concentration of gelatin (typically between 5% and 10% by weight) results in a firmer texture. Gelatin is usually dissolved in hot water or juice and mixed with other ingredients before being poured into molds. Gelatin provides a smooth, melt-in-the-mouth feel that is highly sought after in traditional gummies.
Plant-based gels like agar-agar, derived from seaweed, offer a vegetarian alternative, providing a similar texture to gelatin but often requiring higher concentrations, around 1.3 times more than gelatin, to achieve the same gelling effect. The texture can be firmer and less flexible. Agar-agar is also mixed with hot liquid but sets at room temperature, offering a firmer texture.
Pectin, a fiber found in fruit peels, is another alternative, especially popular in fruit-flavored gummies. It requires the presence of sugar and acid to set and is often used in lower concentrations, around 0.5% to 1.5%. The firmness increases with the amount of pectin, but the texture remains distinctly different from gelatin-based gummies. Pectin-based gummies tend to have a softer, more jelly-like consistency and are ideal for achieving a 'fruitier' texture.
Adjusting the ratio of these gelling agents allows manufacturers to tailor the texture of gummies to specific preferences, from soft and tender to firm and chewy.
1.2 Sweeteners in Gummies
A variety of sweeteners are used in gummies to cater to different tastes and dietary needs:
Sucrose (table sugar) is the most common, providing a classic sweet taste and contributing to the gummy's structure.
High fructose corn syrup offers a similar sweetness and texture but at a lower cost.
Sugar alcohols like xylitol and erythritol are used as sugar-free options, offering a sweet taste without the calories but can have a laxative effect if consumed in large quantities.
Stevia and monk fruit extracts are natural, no-calorie sweeteners gaining popularity for their health benefits, though they can impart a distinct aftertaste.
Choosing the right sweetener depends on several factors, including cost, health considerations, and taste preferences:
For low-cost production: High fructose corn syrup is recommended due to its affordability and similar sweetening power to sucrose.
For health-conscious products: Stevia and monk fruit extracts are excellent choices, offering natural sweetness without calories. Sugar alcohols like xylitol and erythritol are also good options for sugar-free gummies, though they should be used cautiously due to potential digestive sensitivity in some consumers.
For sugar-free gummies: Sugar alcohols such as xylitol and erythritol are ideal, providing sweetness without affecting blood sugar levels significantly.
For premium taste and quality: Sucrose (table sugar) remains the gold standard for its unrivaled natural sweet taste and its role in the texture and structure of gummies.
For the most cutting-edge, high-quality option: Monk fruit extract is gaining popularity for its natural origin, potent sweetness with no calories, and minimal impact on blood sugar levels, though it comes at a higher cost.
Manufacturers must weigh these factors against their target market and product positioning to select the most appropriate sweetener.
1.3 Colorings and Flavorings
Colorings and flavorings are critical for making gummies visually appealing and tasty:
Natural colorings like beet juice, turmeric, and spirulina offer vibrant colors without the health concerns associated with synthetic dyes. However, their colors can be less intense and more variable.
Artificial colorings provide brighter, more consistent hues but have been linked to health issues in sensitive individuals.
Natural flavorings are derived from fruits, herbs, and other natural sources, offering authentic tastes but can be more expensive and less stable under heat.
Artificial flavorings are more cost-effective and provide consistent flavors, but they might not offer the same depth as natural options.
Both colorings and flavorings can impact health, with natural options generally being safer but sometimes less effective in delivering intense colors and flavors. Consumers are increasingly preferring natural additives due to health concerns associated with synthetic alternatives.

1.4 Nutritional Content in Gummies
Gummies can be fortified with vitamins, minerals, and other nutritional supplements, making them not just a treat but a potential health supplement. The optimal nutritional content varies depending on the target demographic and purpose. An ideal nutritional profile balances taste, texture, and health benefits without compromising the gummy's structural integrity.
Over-fortification can lead to a decline in sensory qualities, such as taste and mouthfeel, and may pose health risks if consumption exceeds recommended daily intakes. Conversely, under-fortification may render the nutritional claims negligible, failing to provide any meaningful health benefits.
For example, adding too much vitamin C can lead to a sour taste and potentially degrade the gelatin or pectin structure, affecting the gummy's texture. Adequate levels should be determined based on the RDA for the vitamin(usually around 60mg for adults) while considering the serving size and intended consumption pattern of the gummies.
The optimal nutritional profile in gummies is one that achieves a balance, providing a meaningful amount of vitamins and minerals while retaining the candy's appealing taste and texture. This requires careful formulation and testing to ensure that the addition of nutrients does not negatively impact the gummy's quality. For instance, calcium and vitamin D for bone health can be incorporated in amounts that provide a significant portion of their RDA without compromising the gummy's structure or flavor.
Balancing the nutritional content and sensory qualities in gummies is a complex process that involves understanding the interactions between various ingredients and how they affect the final product's appeal and health benefits.
2. Quality Gummy Manufacturing Process
2.1 Ingredient Mixing
The gummy manufacturing process begins with the precise mixing of ingredients. The gelatin (or plant-based alternatives, Pectin) is first dissolved in water or juice at a controlled temperature to ensure uniformity. Sweeteners, flavorings, and colorings are then added according to the recipe's specific ratios. The mixture is stirred continuously to prevent any clumps from forming and to ensure a homogeneous blend. Key technical aspects include maintaining the correct temperature to facilitate proper dissolution of gelatin (or plant-based alternatives, Pectin) and prevent degradation of heat-sensitive components like certain vitamins or flavorings.

2.2 Molding and Cooling
Once the mixture is ready, it's poured into molds. These molds can be made from various materials, such as silicone or plastic, and are often coated with a food-grade release agent to facilitate easier demolding. The filled molds are then cooled, either at room temperature or in a refrigerated environment, to allow the gummies to set. Cooling must be evenly applied to ensure consistent texture and prevent any deformation of shapes. The cooling time can vary but is crucial for achieving the desired firmness and chewiness of the gummies.
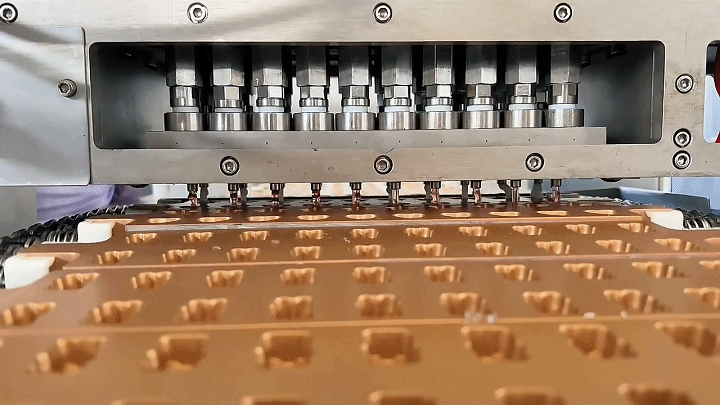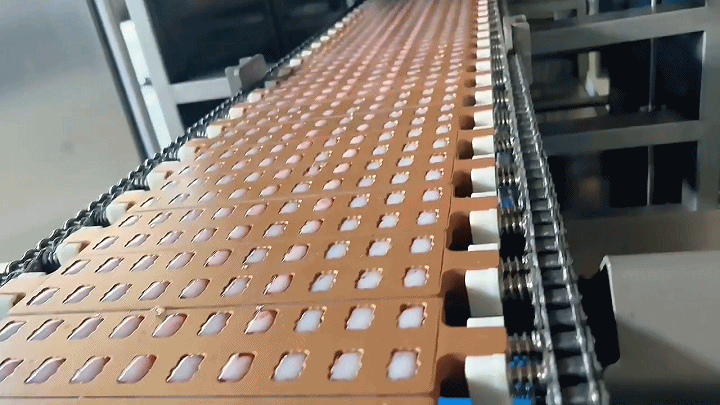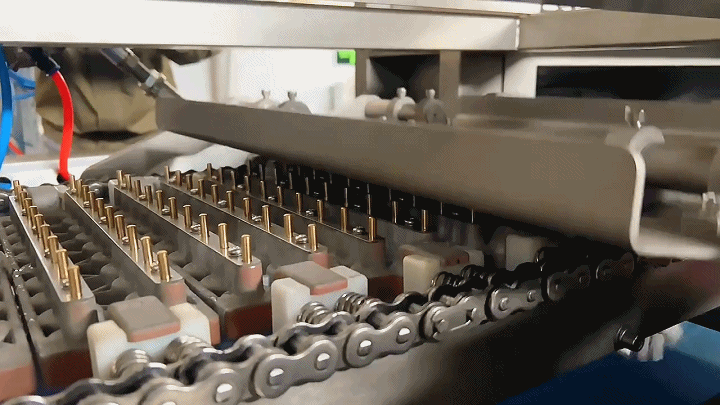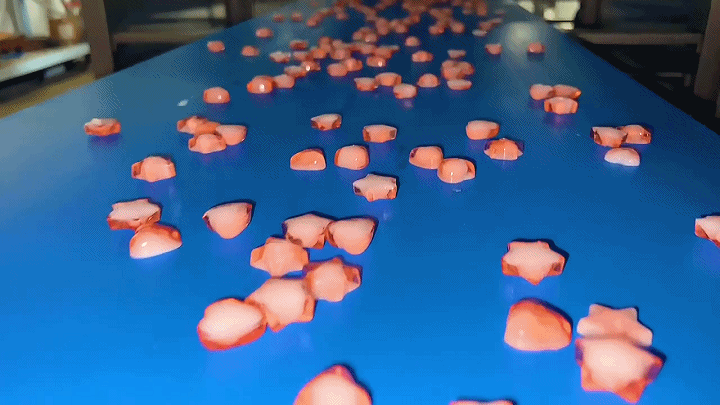
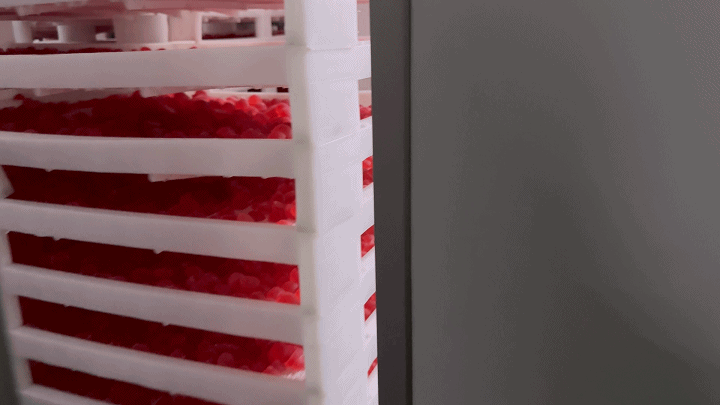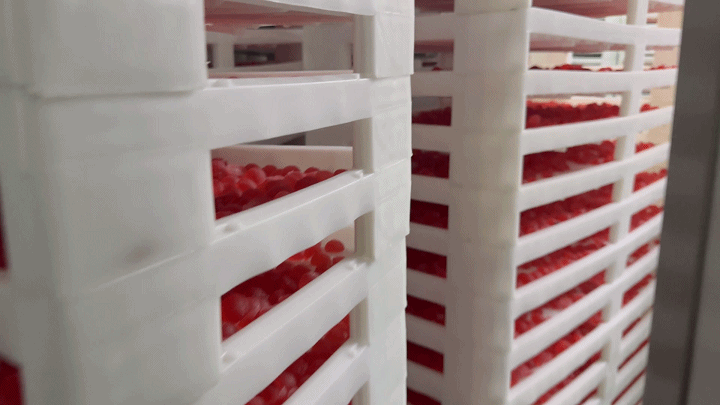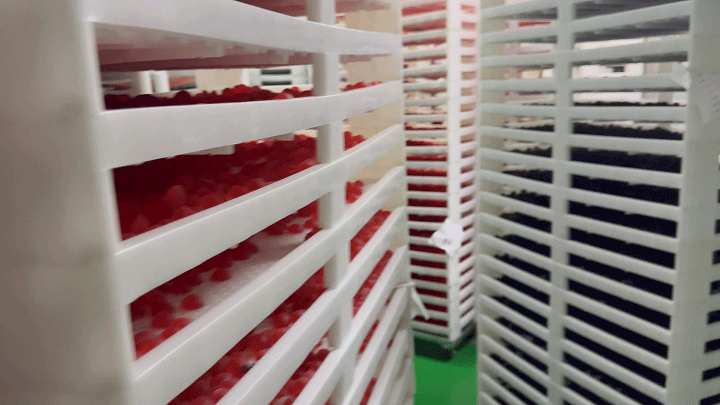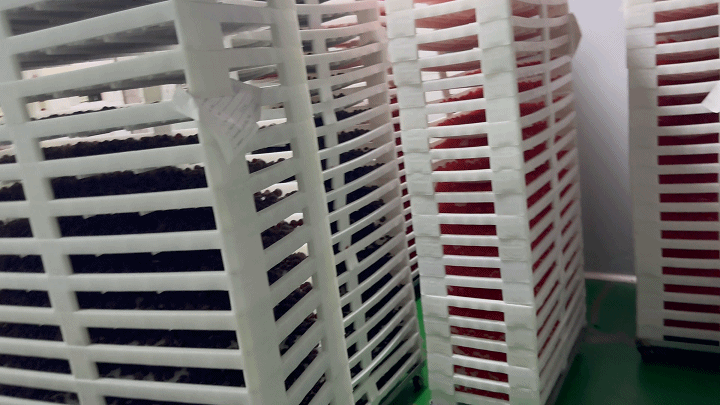
2.3 Demolding and Drying
After the gummies have set and cooled, they are carefully removed from the molds in the demolding process. This step requires precision to maintain the integrity of each gummy's shape. Following demolding, the gummies undergo a drying process to remove any excess moisture. This step is critical for extending the shelf life of the product and enhancing its texture. Controlled drying environments are used to ensure gummies do not lose their shape or stick together.
2.4 Coating
Post-drying, gummies are often coated to prevent sticking, enhance appearance, or add an additional flavor layer. Common coatings include sugar, sour sugar, or a thin layer of oil or wax. The choice of coating depends on the desired finish and taste profile. The coating process not only improves the tactile and taste sensations but also serves as a barrier against moisture, further extending the product's shelf life.

2.5 Packaging
The final step in the gummy manufacturing process is packaging, which is crucial for maintaining freshness and extending shelf life. The packaging process typically involves:
Bottling: Gummies are carefully placed into bottles or jars, ensuring that the container is filled without damaging the product.
Capping: Bottles or jars are then securely sealed with caps to prevent exposure to air, which can degrade the product's quality.
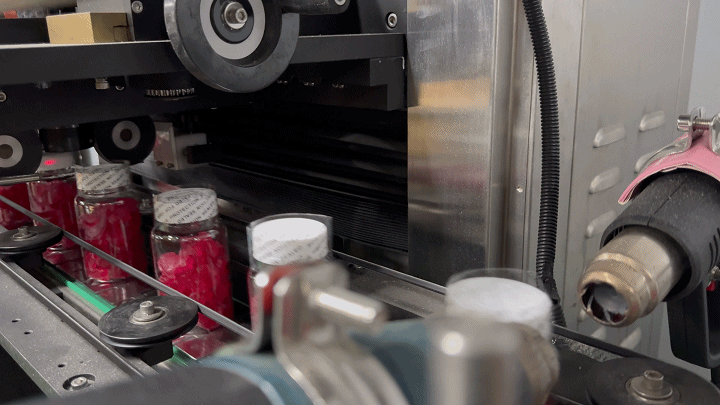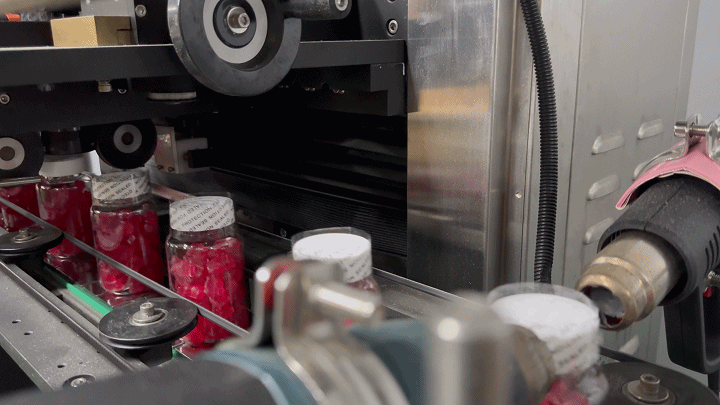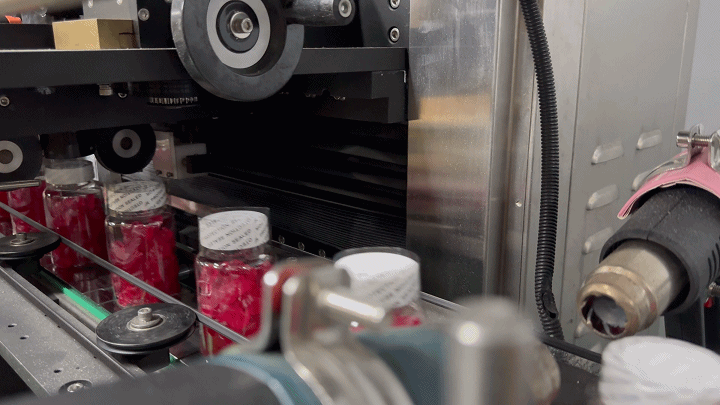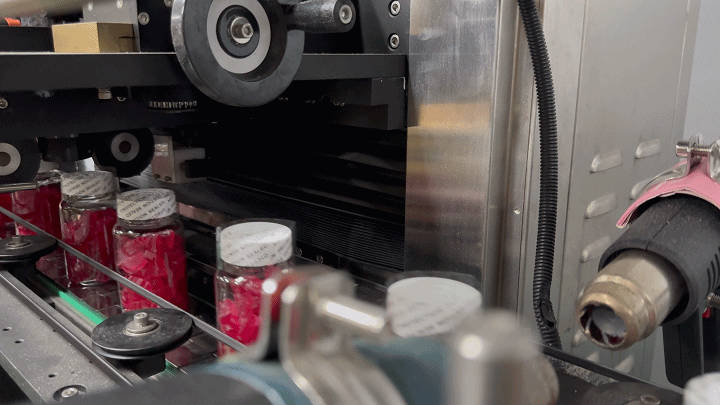
Labeling: The final step involves applying labels that provide product information, nutritional facts, and branding. The labeling must adhere to regulatory standards and be durable enough to withstand handling and transportation.

2.6 Technical and Scientific Principles
The manufacturing of gummies involves a series of precise technical and scientific principles. Temperature control is paramount throughout the process to ensure the proper dissolution of gelatin and to maintain the stability of other ingredients. The rheology, or flow behavior, of the gummy mixture is critical during the mixing and molding stages to achieve the desired texture. The drying process involves an understanding of moisture activity and how it affects product stability and texture. Throughout the process, quality control measures are in place to monitor the consistency, texture, and flavor of the gummies, ensuring that each batch meets the high standards set by the manufacturer.
3. Quality Control and Safety Standards in Gummy Manufacturing
3.1 Quality Control Measures
Quality control (QC) in gummy manufacturing is a comprehensive process that ensures the final product meets the established standards of quality and safety. The QC measures encompass various tests and controls at different stages of production:
Ingredient Testing: Before the production process begins, all raw materials are tested for purity, quality, and compliance with food safety standards. This includes checking for any contaminants in the gelatin or plant-based gels, ensuring sweeteners are within acceptable purity levels, and verifying the quality of flavorings and colorings.
In-process Controls: During the manufacturing process, several control measures are implemented. These include monitoring the temperature and consistency of the gummy mixture, ensuring the molds are correctly filled, and verifying the settings on cooling and drying equipment to ensure consistency across batches.
Finished Product Testing: Once the gummies are manufactured, they undergo a series of tests to assess their texture, firmness, flavor, and appearance. This may include laboratory testing for shelf life and stability under various storage conditions.
Packaging Inspection: The integrity of the packaging is crucial for maintaining the quality of the gummies. Inspections ensure that the packaging is properly sealed and labeled, providing a barrier against contamination and ensuring that the product information is accurate and compliant with regulations.
Implementing these QC measures helps in identifying and addressing any deviations from the set standards, ensuring that every batch of gummies is of high quality and safe for consumption.
3.2 Food Safety and Gummy Production Standards
Adherence to food safety and manufacturing standards is paramount in the production of gummies. These standards are designed to ensure that food products are safe for consumption and produced under hygienic conditions:
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP): GMPs are guidelines that provide a framework for manufacturing processes, ensuring that products are consistently produced and controlled according to quality standards. For gummy manufacturing, this includes controlling environmental conditions to prevent cross-contamination, ensuring equipment is properly maintained and sanitized, and training staff in hygiene and food safety practices.
Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Regulations: In the United States, the FDA sets regulations for food products, including gummies. These regulations cover aspects such as ingredient labeling, food additives, and packaging. Compliance with FDA regulations is essential to ensure that the gummies are safe for consumption and free from harmful substances.
Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP): HACCP is a management system that addresses food safety through the analysis and control of biological, chemical, and physical hazards from raw material production, procurement, and handling, to manufacturing, distribution, and consumption of the finished product. Implementing HACCP principles helps in identifying potential food safety hazards and establishing critical control points to prevent, eliminate, or reduce these hazards to acceptable levels.
Compliance with these standards not only ensures the safety and quality of the gummies but also builds consumer trust and confidence in the brand. Regular audits and certifications by third-party organizations can further validate a manufacturer's commitment to maintaining high standards of food safety and quality.



One Response